Insulin plays a key role in regulating your body’s metabolism and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. By adopting holistic approaches, you can enhance your metabolic health and improve insulin sensitivity. This guide will explore how lifestyle choices, nutrition, and mindfulness practices can support your metabolic processes. Whether you’re looking to stabilize your energy levels or maintain your overall well-being, understanding these interconnected elements will empower you to take charge of your health journey. Dive in to discover practical strategies that can make a significant impact on your metabolic function.
Key Takeaways:
- Holistic approaches integrate nutrition, physical activity, stress management, and sleep quality to support metabolic health and enhance insulin sensitivity.
- Whole, unprocessed foods rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve metabolic function.
- Regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercises and strength training, plays a vital role in maintaining healthy insulin sensitivity.
- Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep contribute significantly to hormonal balance and can reduce insulin resistance.
- An individualized approach is important, as factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and existing health conditions can influence metabolic health outcomes.
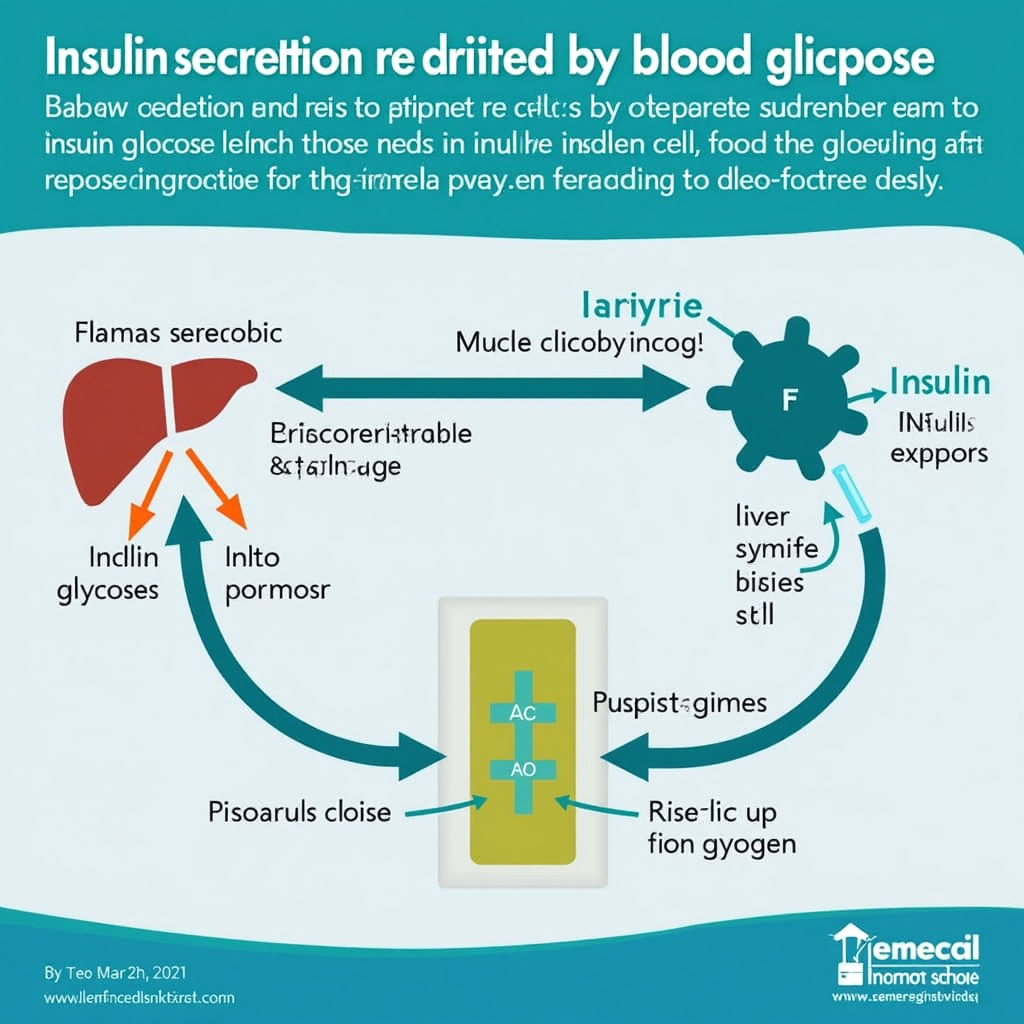
The Biochemical Pathways of Insulin Response
Understanding the biochemical pathways of insulin response reveals crucial mechanisms that regulate your energy metabolism. Insulin acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose to enter for energy use or storage. This process involves complex interactions between your pancreas, liver, muscle, and fat tissues, all contributing to maintaining balance in blood glucose levels. Recognizing these pathways is vital for tailoring lifestyle choices that promote metabolic health.
Insulin Secretion and Action
Insulin secretion is primarily driven by blood glucose levels, with the beta cells in the pancreas detecting increases and releasing insulin accordingly. Once secreted, insulin binds to insulin receptors on cells, triggering pathways that facilitate glucose uptake and storage. For instance, muscle cells use this hormone to absorb glucose, while the liver stores it as glycogen. Ensuring that these processes run smoothly is key to maintaining optimal metabolic health.
Factors Influencing Insulin Sensitivity
Multiple factors can enhance or diminish insulin sensitivity, impacting how effectively your body responds to insulin. Genetics play a role, alongside lifestyle choices such as diet, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Chronic inflammation, stress levels, and hormonal imbalances can also contribute significantly to insulin sensitivity. Understanding these influences allows you to adopt strategies that support insulin function and overall health.
- Diet: A nutrient-rich diet high in fiber and low in refined carbs fosters better insulin sensitivity.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances muscle uptake of glucose.
- Sleep: Quality sleep plays a fundamental role in regulating metabolic hormones.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to higher cortisol, adversely affecting insulin action.
- Age: Insulin sensitivity tends to decrease with aging.
Focusing on these factors can lead to meaningful improvements in your insulin sensitivity. For example, engaging in just 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week can significantly improve your body’s responsiveness to insulin. Dietary adjustments such as incorporating healthy fats, lean proteins, and whole grains can stabilize blood sugar levels. Also, while genetic factors may be beyond your control, making mindful lifestyle changes can produce positive results over time.
- Genetics: Family history of diabetes can predispose individuals to insulin resistance.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is linked to decreased insulin sensitivity.
- Bacterial flora: A diverse gut microbiome can influence insulin responsiveness.
- Medications: Certain medications can negatively impact insulin sensitivity.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like PCOS and sleep apnea can exacerbate insulin resistance.
Nutrient Timing: Unlocking Metabolic Flexibility
Nutrient timing involves strategically scheduling your meals and snacks to optimize metabolic flexibility and enhance insulin sensitivity. By coordinating when you eat with your daily activities and energy demands, you can improve your body’s ability to utilize nutrients efficiently. Tailoring your intake to your biological rhythms not only supports blood sugar control but also enhances overall energy and performance.
The Role of Meal Composition
Meal composition significantly influences insulin sensitivity and metabolism. A balanced plate incorporating lean proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates ensures a steadier release of glucose into your bloodstream, which can prevent spikes in insulin levels. For instance, adding fiber-rich foods, like vegetables and whole grains, aids in slowing down digestion, providing sustained energy and optimal metabolic function.
Strategic Eating Patterns for Optimal Insulin Use
Adopting strategic eating patterns can maximize your body’s ability to use insulin effectively. Distributing your food intake throughout the day, with regular meals and well-timed snacks, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Incorporating time-restricted feeding, where you limit eating to a specific window, may enhance your metabolic response, as studies suggest this can positively influence insulin sensitivity while also promoting fat loss.
Implementing these patterns not only helps regulate insulin response but also aligns with your body’s natural rhythms. For example, consuming most of your calories earlier in the day aligns with higher insulin sensitivity after fasting overnight, making breakfast the perfect time for carbohydrate-rich meals. Research indicates that those who practice such meal timing often experience improved insulin action and reduced cravings, leading to a healthier metabolic state. Over time, this approach can cultivate a more resilient metabolism, supporting better weight management and overall health.
Exercise as Medicine: Enhancing Metabolic Capacity
Engaging in regular physical activity significantly boosts metabolic health and insulin sensitivity. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you effectively enhance your body’s ability to metabolize glucose and fats. This not only helps prevent metabolic disorders but promotes overall wellness. Specific types of exercise, such as resistance training and aerobic activities, play unique roles in optimizing your metabolic capacity and should be tailored to meet your individual health goals.
The Effects of Resistance Training
Resistance training, often overlooked in favor of cardio, is a powerhouse for improving insulin sensitivity. By increasing muscle mass, you enhance your body’s ability to utilize glucose effectively. Studies show that just two to three sessions of strength training a week can lead to significant improvements in insulin sensitivity, helping maintain stable blood sugar levels. This form of exercise boosts metabolic rate even at rest, translating into long-term benefits for your energy expenditure.
Aerobic Activity’s Role in Insulin Sensitivity
Aerobic activity plays a key part in enhancing insulin sensitivity, importantly improving how your cells respond to the hormone. Engaging in moderate to vigorous aerobic exercises like running, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week can lead to marked improvements. Research indicates these activities can lower insulin resistance by up to 30%, making them important for effective metabolic management.
Incorporating aerobic activities into your routine not only supports weight management but also enhances cardiovascular health, both of which are linked to better insulin sensitivity. Regular aerobic exercise increases the number of glucose transporters in your muscle cells, facilitating a more effective uptake of glucose following meals. This process helps regulate blood sugar levels and decreases the risk of insulin resistance, reinforcing the importance of maintaining a consistent exercise schedule. By prioritizing a blend of both resistance and aerobic exercises, you set yourself up for optimal metabolic health.
Stress and Sleep: Unseen Regulators of Metabolic Health
Effective management of stress and prioritizing sleep can significantly enhance metabolic health and improve insulin sensitivity. Chronic stress triggers physiological responses that can negatively impact your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. Similarly, insufficient sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances, ultimately sabotaging your metabolic processes. By understanding and addressing these two factors, you can create a solid foundation for optimal health and well-being.
The Impact of Cortisol on Insulin Dynamics
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, plays a pivotal role in how your body reacts to stressors. Elevated cortisol levels can interfere with insulin signaling, resulting in increased insulin resistance and higher blood sugar levels. This dynamic can set the stage for metabolic dysfunction, making it crucial to find strategies for stress reduction to maintain or improve your insulin efficacy.
Sleep’s Role in Hormonal Balance and Metabolic Function
Quality sleep is a cornerstone for maintaining hormonal balance and optimal metabolic function. Sleep deprivation can disrupt circadian rhythms, leading to imbalances in hormones such as ghrelin and leptin, both of which regulate appetite and energy balance. This disruption can cause you to crave more calorie-dense foods, ultimately compromising your metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Research indicates that just one week of inadequate sleep can lead to measurable changes in insulin sensitivity, with participants showing 30 to 40% decreased insulin responsiveness (Nedeltcheva, 2009). Furthermore, deep sleep stages are critical for the release of growth hormone, which aids in metabolism regulation. Prioritizing 7-9 hours of quality sleep not only supports hormone production but also nurtures the restorative processes your body needs to function optimally, enhancing overall metabolic health.
Mindfulness and Behavior Change: Cultivating Sustainable Habits
Mindfulness practices foster a heightened awareness of your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, paving the way for lasting change. By integrating mindfulness into your daily routine, you can identify patterns that contribute to poor metabolic health and replace them with healthier choices that promote insulin sensitivity. This shift is not about drastic measures but rather about cultivating small, sustainable habits that gradually lead to improved health outcomes.
Techniques for Stress Reduction and Awareness
Incorporating techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and increase your awareness of emotional triggers. These practices not only promote relaxation but also enhance your capacity to respond to cravings or emotional eating, creating a more mindful approach to food and health. Engaging in mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) has shown promising results, with studies indicating it can lower cortisol levels and improve metabolic markers.
Building a Supportive Environment for Healthy Choices
A supportive environment plays a vital role in making healthier choices accessible and sustainable. Surrounding yourself with positive influences, such as friends who prioritize health or a community that engages in regular physical activity, can significantly impact your likelihood of success. Furthermore, making intentional decisions about your home and workplace—like stocking healthy snacks and reducing exposure to processed foods—creates an atmosphere that aligns with your health goals.
Creating a supportive environment involves more than just choosing the right foods. Engage family and friends in your journey by sharing your goals and inviting them to join you in healthy activities. For instance, cooking nutritious meals together not only strengthens connections but also builds a communal commitment to health. Utilize resources like meal planning apps or community fitness classes that foster accountability. By nurturing an ecosystem that promotes wellness, you empower yourself to make healthier choices seamlessly integrated into your daily life.
To wrap up
Hence, embracing holistic approaches to metabolic health and insulin sensitivity can profoundly enhance your well-being. By integrating balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep into your daily routine, you empower your body to function optimally. These lifestyle changes not only support healthy insulin levels but also promote overall vitality and resilience. Adopting this comprehensive perspective allows you to take charge of your health and pave the way for a more energized life.
FAQ
Q: What is metabolic health, and why is it important?
A: Metabolic health refers to how well your body’s systems work together to maintain balanced levels of blood sugar, lipid levels, and blood pressure, among other factors. Good metabolic health decreases the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity, contributing to overall well-being and longevity. It’s vital to cultivate a balanced lifestyle that supports metabolic health, including nutrition, physical activity, and stress management.
Q: How can diet influence insulin sensitivity?
A: Diet plays a significant role in insulin sensitivity. Consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods such as vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains can enhance insulin sensitivity. Conversely, high sugar and refined carbohydrate intake may lead to insulin resistance. Including foods rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats can support metabolic health by improving how the body utilizes insulin.
Q: What holistic practices can support metabolic health?
A: Holistic practices that support metabolic health include mindfulness and stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises. These practices can lower cortisol levels, which influence insulin sensitivity. Additionally, adequate sleep, regular physical activity, and community support all contribute to a well-rounded approach to improving metabolic health.
Q: Can supplementation play a role in improving insulin sensitivity?
A: Some supplements may support insulin sensitivity, including magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, and alpha-lipoic acid. However, it’s important to discuss any supplementation with a healthcare provider to ensure safety and appropriateness. A balanced diet rich in nutrients often provides adequate support for insulin sensitivity, and supplements should not replace healthy food choices.
Q: How can physical activity improve metabolic health?
A: Regular physical activity enhances metabolic health by increasing muscle mass, improving insulin sensitivity, and promoting better glucose uptake by the cells. Both aerobic exercise and resistance training contribute positively to metabolic health. Engaging in consistent physical activity helps regulate weight, reduces inflammation, and enhances cardiovascular health, creating an overall beneficial effect on metabolic processes.

